Maximum Sum Area
19 Mar 2013As a follow up to my previous post where we found the maximum sum subsequence of a one dimensional array, in this post the idea will be extended to cover 2d arrays or grids of numbers.
Instead of finding the subsequence of the array that contains the maximum sum, now the region of the array with the maximum sum will be found. For example in the image below, the region of the array with the largest sum is found to be enclosed by the points (1,1) and (3,2).
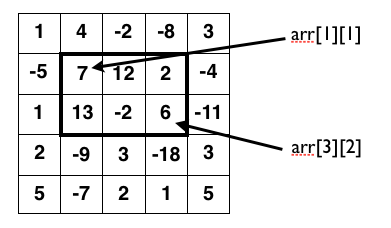
Here is the algorithm. Note that this is massively inefficient with an order of O(n^6) - meaning that if we double the input size, the time taken calculate the result will increase by a factor of 64 (2^6).
/\*\*
- Sum an area of a 2d array starting from specified coordinates
-
- @param i
- x1
- @param j
- y1
- @param k
- x2
- @param l
- y2
- @param arr
- The 2d array to sum the elements of
- @return The sum of the array from (i, k) to (j, l)
\*/
private static int sumArea(int i, int j, int k, int l, int[][] arr) {
int sum = 0;
for (int m = i; m <= k; m++) {
for (int n = j; n <= l; n++) {
sum = sum + arr[m][n]
}
}
return sum;
}
/\*\* Calculate the maximum sum region of a 2d array Note this algorithm is extremely inefficient - O(n^6)
- @param arr
- The 2d array to find the maximum sum region of
- @return An array containing { x1, y1, x2, y2, sum }
\*/
public static int[]] maxSumArea(int[][] arr) {
int tmp;
int maxiSoFar = 0;
int maxjSoFar = 0;
int maxkSoFar = 0;
int maxlSoFar = 0;
int maxSumSoFar = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < arr[0].length; j++) {
for (int k = i; k < arr.length; k++) {
for (int l = j; l < arr[0].length; l++) {
tmp = sumArea(i, j, k, l, arr);
if (tmp > maxSumSoFar) {
maxiSoFar = i;
maxjSoFar = j;
maxkSoFar = k;
maxlSoFar = l;
maxSumSoFar = tmp;
}
}
}
}
}
return new int[] { maxiSoFar, maxjSoFar, maxkSoFar, maxlSoFar, maxSumSoFar };
}
Here is also a small tester method displaying how the method can be used with the same 2d as shown in the example above -
public static void main(String[] args) {
final int[][] testArray = {
{ 1, 4, -2, -8, 3 },
{ -5, 7, 12, 2, -4 },
{ 1, 13, -2, 6, -11 },
{ 2, -9, 3, -18, 3 },
{ 5, -7, 2, 1, 5 }
};
int[] result = maxSumArea(testArray);
System.out.printf("x1 = %d; y1 = %d; x2 = %d; y2 = %d\n", result[0], result[1], result[3], result[2]);
System.out.println("Maximum sum area = " + result[4]);
System.out.println();
for (int i = result[0]; i <= result[2]; i++) {
for (int j = result[1]; j <= result[3]; j++) {
System.out.print(testArray[i][j] + "\t");
}
System.out.println();
}
}Which generates the output -
x1 = 1;
y1 = 1;
x2 = 3;
y2 = 2
Maximum sum area = 38 7 12 2 13 -2 6